Sergio在使用Java和RDBMS(如Oracle)开发企业级应用程序方面有十几年的经验, PostgreSQL, and MySQL.
Sergio在使用Java和RDBMS(如Oracle)开发企业级应用程序方面有十几年的经验, PostgreSQL, and MySQL.
本文是关于如何设置的服务器端实现的指南 JSON Web Token (JWT) - OAuth2 authorization framework using Spring Boot and Maven.
建议对OAuth2有一个初步的了解,可以通过阅读上面链接的草案或在网上搜索有用的信息 this or this.
OAuth2是一个授权框架,取代了2006年创建的第一个版本OAuth. 它定义了客户机和一个或多个HTTP服务之间的授权流,以便获得对受保护资源的访问.
OAuth2 defines the following server-side roles:
JSON Web Token, or JWT, 索赔的陈述说明书是否要在双方之间转让. 声明被编码为JSON对象,用作加密结构的有效负载, enabling the claims to be digitally signed or encrypted.
包含结构可以是JSON Web Signature (JWS)或JSON Web Encryption (JWE)。.
可以选择JWT作为OAuth2协议中使用的访问和刷新令牌的格式.
由于以下特性,OAuth2和JWT在过去几年中获得了巨大的普及:
However, 如果以下考虑对项目很重要,OAuth2和JWT并不总是最佳选择:
OAuth2的主要特性之一是引入了一个授权层,以便将授权过程与资源所有者分开, for the sake of simplicity, 本文的结果是构建一个模拟所有应用程序的应用程序 resource owner, authorization server, and resource server roles. 因此,通信将只在两个实体之间流动,即服务器和客户端.
这种简化应该有助于集中在文章的目的,即.e. the setup of such a system in a Spring Boot’s environment.
The simplified flow is described below:
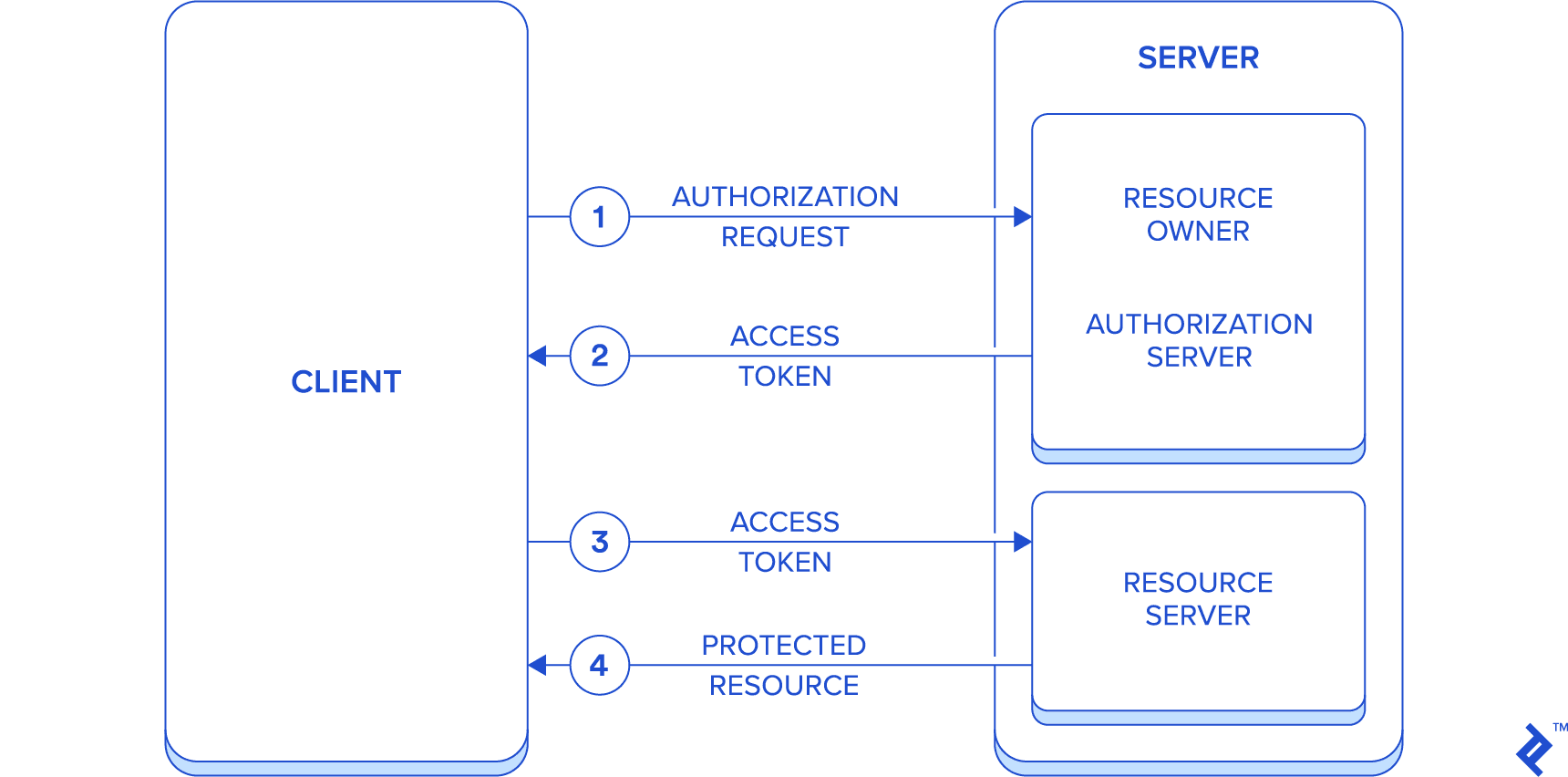
首先,简要介绍了本项目选用的技术栈.
The project management tool of choice is Maven,但由于项目的简单性,应该不难切换到其他工具,如 Gradle.
In the article’s continuation, we focus on Spring Security aspects only, 但是所有的代码摘录都是从一个完全工作的服务器端应用程序中提取的,该应用程序的源代码可以在公共存储库中与使用其REST资源的客户端一起获得.
Spring Security是一个框架,为基于Spring的应用程序提供几乎是声明式的安全服务. 它的根源是从春天的第一个开始,它被组织为一组模块,因为有很多不同的 security technologies covered.
让我们快速了解一下Spring Security体系结构(可以找到更详细的指南) here).
Security is mostly about authentication, i.e. the verification of the identity, and authorization, the grant of access rights to resources.
Spring security supports a huge range of authentication models, either provided by third parties or implemented natively. A list can be found here.
Regarding authorization, three main areas are identified:
The basic interface is AuthenticationManager which is responsible to provide an authentication method. The UserDetailsService is the interface related to user’s information collection, 在标准JDBC或LDAP方法的情况下,哪些可以直接实现或在内部使用.
The main interface is AccessDecisionManager; which implementations for all three areas listed above delegate to a chain of AccessDecisionVoter. 后一种接口的每个实例都表示对象之间的关联 Authentication (一个用户标识,命名为principal)、一个资源和一个集合 ConfigAttribute, 描述资源所有者如何允许访问资源本身的一组规则, maybe through the use of user roles.
web应用程序的安全性是使用上面描述的servlet过滤器链中的基本元素实现的, and the class WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 公开为表示资源访问规则的声明性方式.
Method security is first enabled by the presence of the @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true) annotation, 然后通过使用一组专门的注释来应用于每个要保护的方法,如 @Secured, @PreAuthorize, and @PostAuthorize.
Spring Boot在此基础上增加了一系列固执己见的应用程序配置和第三方库,以便在保持高质量标准的同时简化开发.
现在让我们继续讨论最初的问题,设置一个使用Spring Boot实现OAuth2和JWT的应用程序.
虽然Java世界中存在多个服务器端OAuth2库(可以找到一个列表) here), 基于Spring的实现是自然的选择,因为我们希望它能很好地集成到Spring Security体系结构中,从而避免为使用它而处理大量的底层细节.
所有与安全相关的库依赖都由Maven在Spring Boot的帮助下处理, 在maven的配置文件中,哪一个组件是唯一需要显式版本的 pom.xml (i.e. 库版本由Maven自动推断,选择与插入的Spring Boot版本兼容的最新版本).
Find below the excerpt from maven’s configuration file pom.xml containing the dependencies related to Spring Boot security:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-security
org.springframework.security.oauth.boot
spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure
2.1.0.RELEASE
应用程序既充当OAuth2授权服务器/资源所有者,又充当资源服务器.
The protected resources (as resource server) are published under /api/ 路径,而身份验证路径(作为资源所有者/授权服务器)映射到 /oauth/token, following proposed default.
App’s structure:
security package containing security configurationerrors package containing error handlingusers, glee REST资源包,包括模型、存储库和控制器接下来的段落将介绍上面提到的三个OAuth2角色的配置. The related classes are inside security package:
OAuthConfiguration, extending AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter
ResourceServerConfiguration, extending ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter
ServerSecurityConfig, extending WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
UserService, implementing UserDetailsService
Authorization server behavior is enabled by the presence of @EnableAuthorizationServer annotation. 它的配置与与资源所有者行为相关的配置合并,并且两者都包含在类中 AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter.
The configurations applied here are related to:
ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer)
inMemory or jdbc methodsclientId and clientSecret (encoded with the chosen PasswordEncoder bean) attributesaccessTokenValiditySeconds and refreshTokenValiditySeconds attributesauthorizedGrantTypes attributescopes methodAuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer)
accessTokenConverter
UserDetailsService and AuthenticationManager interfaces to perform authentication (as resource owner)package net.reliqs.gleeometer.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.configurers.ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableAuthorizationServer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.store.JwtAccessTokenConverter;
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
公共类OAuthConfiguration扩展AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter
private final AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
private final PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
private final UserDetailsService userService;
@Value("${jwt.clientId:glee-o-meter}")
private String clientId;
@Value("${jwt.client-secret:secret}")
private String clientSecret;
@Value("${jwt.signing-key:123}")
private String jwtSigningKey;
@Value("${jwt.accessTokenValidititySeconds:43200}") // 12 hours
private int accessTokenValiditySeconds;
@Value("${jwt.authorizedGrantTypes:密码,authorization_code refresh_token}”)
private String[] authorizedGrantTypes;
@Value("${jwt.refreshTokenValiditySeconds:2592000}") // 30 days
private int refreshTokenValiditySeconds;
公共OAuthConfiguration(AuthenticationManager, PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder, UserDetailsService userService) {
this.authenticationManager = authenticationManager;
this.passwordEncoder = passwordEncoder;
this.userService = userService;
}
@Override
公共无效配置(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer客户端)抛出异常{
clients.inMemory()
.withClient(clientId)
.secret(passwordEncoder.encode(clientSecret))
.accessTokenValiditySeconds(accessTokenValiditySeconds)
.refreshTokenValiditySeconds(refreshTokenValiditySeconds)
.authorizedGrantTypes(authorizedGrantTypes)
.scopes("read", "write")
.resourceIds("api");
}
@Override
公共无效配置(最终authorizationserverendpointsconfiguratorendpoints) {
endpoints
.accessTokenConverter(accessTokenConverter())
.userDetailsService(userService)
.authenticationManager(authenticationManager);
}
@Bean
JwtAccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter() {
JwtAccessTokenConverter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
return converter;
}
}
下一节描述应用于资源服务器的配置.
The resource server behavior is enabled by the use of @EnableResourceServer annotation and its configuration is contained in the class ResourceServerConfiguration.
这里唯一需要的配置是资源标识的定义,以便匹配上一个类中定义的客户端访问.
package net.reliqs.gleeometer.security;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableResourceServer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
公共类ResourceServerConfiguration扩展ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter
@Override
公共无效配置(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer资源){
resources.resourceId("api");
}
}
最后一个配置元素是关于web应用程序安全性的定义.
Spring web security configuration is contained in the class ServerSecurityConfig, enabled by the use of @EnableWebSecurity annotation. The @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity permits to specify security on the method level. Its attribute proxyTargetClass is set in order to have this working for RestController因为控制器通常是类,不实现任何接口.
It defines the following:
authenticationProvider
passwordEncoder
HttpSecurity
AuthenticationEntryPoint 以便在标准Spring REST错误处理程序之外处理错误消息 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler
package net.reliqs.gleeometer.security;
import net.reliqs.gleeometer.errors.CustomAccessDeniedHandler;
import net.reliqs.gleeometer.errors.CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, proxyTargetClass = true)
公共类ServerSecurityConfig扩展WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint;
private final UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
公共ServerSecurityConfig(CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint, @Qualifier("userService")
UserDetailsService userDetailsService) {
this.customAuthenticationEntryPoint = customAuthenticationEntryPoint;
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
}
@Bean
public DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider() {
DaoAuthenticationProvider provider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
provider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
provider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);
return provider;
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
@Override
公共AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean()抛出异常{
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/signin/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/glee/**").hasAnyAuthority("ADMIN", "USER")
.antMatchers("/api/users/**").hasAuthority("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/api/**").authenticated()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(customAuthenticationEntryPoint).accessDeniedHandler(new CustomAccessDeniedHandler());
}
}
The code extract below is about the implementation of UserDetailsService 接口,以便提供资源所有者的身份验证.
package net.reliqs.gleeometer.security;
import net.reliqs.gleeometer.users.User;
import net.reliqs.gleeometer.users.UserRepository;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService implements UserDetailsService {
private final UserRepository repository;
public UserService(UserRepository repository) {
this.repository = repository;
}
@Override
loadUserByUsername(String username)抛出UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = repository.findByEmail(username).orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("User not found: " + username));
GrantedAuthority authority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(user.getRole().name());
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getEmail(), user.getPassword(), Arrays.asList(authority));
}
}
下一节是关于REST控制器实现的描述,以便了解如何映射安全约束.
在REST控制器内部,我们可以找到两种方法来为每个资源方法应用访问控制:
OAuth2Authentication passed in by Spring as a parameter@PreAuthorize or @PostAuthorize annotationspackage net.reliqs.gleeometer.users;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import net.reliqs.gleeometer.errors.EntityNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.web.PageableDefault;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PostAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.OAuth2Authentication;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
import java.util.HashSet;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
@Slf4j
@Validated
class UserController {
private final UserRepository repository;
private final PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
UserController(UserRepository repository, PasswordEncoder PasswordEncoder) {
this.repository = repository;
this.passwordEncoder = passwordEncoder;
}
@GetMapping
Page all(@PageableDefault(size = Integer.MAX_VALUE) Pageable Pageable, OAuth2Authentication鉴权){
String auth = (String) authentication.getUserAuthentication().getPrincipal();
String role = authentication.getAuthorities().iterator().next().getAuthority();
if (role.equals(User.Role.USER.name())) {
return repository.findAllByEmail(auth, pageable);
}
return repository.findAll(pageable);
}
@GetMapping("/search")
Page search(@RequestParam String email, Pageable pageable, OAuth2Authentication authentication) {
String auth = (String) authentication.getUserAuthentication().getPrincipal();
String role = authentication.getAuthorities().iterator().next().getAuthority();
if (role.equals(User.Role.USER.name())) {
return repository.findAllByEmailContainsAndEmail(email, auth, pageable);
}
return repository.findByEmailContains(email, pageable);
}
@GetMapping("/findByEmail")
@PreAuthorize("!hasAuthority('USER') || (authentication.principal == #email)")
用户findByEmail(@RequestParam String email, OAuth2Authentication鉴权){
return repository.findByEmail(email).orElseThrow(() -> new EntityNotFoundException(User.class, "email", email));
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
@PostAuthorize("!hasAuthority('USER') || (returnObject != null && returnObject.email == authentication.principal)")
User one(@PathVariable Long id) {
return repository.findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new EntityNotFoundException(User.class, "id", id.toString()));
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
@PreAuthorize("!hasAuthority('USER') || (authentication.principal == @userRepository.findById(#id).orElse(new net.reliqs.gleeometer.users.User()).email)")
无效更新(@PathVariable长id, @有效@RequestBody用户res) {
User u = repository.findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new EntityNotFoundException(User.class, "id", id.toString()));
res.setPassword(u.getPassword());
res.setGlee(u.getGlee());
repository.save(res);
}
@PostMapping
@PreAuthorize("!hasAuthority('USER')")
User create(@Valid @RequestBody User res) {
return repository.save(res);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
@PreAuthorize("!hasAuthority('USER')")
void delete(@PathVariable Long id) {
if (repository.existsById(id)) {
repository.deleteById(id);
} else {
throw new EntityNotFoundException(User.class, "id", id.toString());
}
}
@PutMapping("/{id}/changePassword")
@PreAuthorize("!hasAuthority('USER') || (#oldPassword != null && !#oldPassword.isEmpty() && authentication.principal == @userRepository.findById(#id).orElse(new net.reliqs.gleeometer.users.User()).email)")
void changePassword(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam(required = false) String oldPassword, @Valid @Size(min = 3) @RequestParam String newPassword) {
User user = repository.findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new EntityNotFoundException(User.class, "id", id.toString()));
if (oldPassword == null || oldPassword.isEmpty() || passwordEncoder.matches(oldPassword, user.getPassword())) {
user.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(newPassword));
repository.save(user);
} else {
throw new ConstraintViolationException("old password doesn't match", new HashSet<>());
}
}
}
Spring Security和Spring Boot允许以近乎声明的方式快速设置完整的OAuth2授权/身份验证服务器. 通过直接配置OAuth2客户机的属性,可以进一步缩短设置时间 application.properties/yml file, as explained in this tutorial.
All source code is available in this GitHub repository: spring-glee-o-meter. 在这个GitHub存储库中可以找到一个使用发布资源的Angular客户端: glee-o-meter.
OAuth2是一个授权框架,允许第三方应用程序通过共享访问令牌获得对HTTP服务的有限访问. Its specification supersedes and obsoletes OAuth 1.0 protocol.
JWT stands for JSON Web Token, 在双方当事人之间转让的权利要求的陈述说明. 声明被编码为JSON对象,用作加密结构的有效负载,该结构允许对声明进行数字签名或加密.
Spring Security是一个专注于为基于Spring的应用程序提供身份验证和授权的框架.
Spring Boot是Spring平台和第三方库的一个固执己见的观点,它允许最小化基于Spring的应用程序的配置,同时保持生产级的质量水平.
Castel Maggiore, Metropolitan City of Bologna, Italy
Member since December 11, 2018
Sergio在使用Java和RDBMS(如Oracle)开发企业级应用程序方面有十几年的经验, PostgreSQL, and MySQL.
World-class articles, delivered weekly.
World-class articles, delivered weekly.
Join the Toptal® community.